AP Investigation: Fish billed as local isn’t always local

An Associated Press investigation has found that Sea To Table, a key player in the sustainable food movement, has untrue information in the sourcing of its locally-caught tuna. (June 13)
By ROBIN MCDOWELL, MARGIE MASON and MARTHA MENDOZA | Jun. 15, 2018
MONTAUK, N.Y. (AP) — Even after winter storms left East Coast harbors thick with ice, some of the country’s top chefs and trendy restaurants were offering sushi-grade tuna supposedly pulled in fresh off the coast of New York.
But it was just an illusion. No tuna was landing there. The fish had long since migrated to warmer waters.
In a global industry plagued by fraud and deceit, conscientious consumers are increasingly paying top dollar for what they believe is local, sustainably caught seafood. But even in this fast-growing niche market, companies can hide behind murky supply chains that make it difficult to determine where any given fish comes from. That’s where national distributor Sea To Table stepped in, guaranteeing its products were wild and directly traceable to a U.S. dock — and sometimes the very boat that brought it in.
However, an Associated Press investigation found the company was linked to some of the same practices it vowed to fight. Preliminary DNA tests suggested some of its yellowfin tuna likely came from the other side of the world, and reporters traced the company’s supply chain to migrant fishermen in foreign waters who described labor abuses, poaching and the slaughter of sharks, whales and dolphins.
The New York-based distributor was also offering species in other parts of the country that were illegal to catch, out of season and farmed.
Over the years, Sea To Table has become a darling in the sustainable seafood movement, building an impressive list of clientele, including celebrity chef Rick Bayless, Chopt Creative Salad chain, top universities and the makers of home meal kits such as HelloFresh.
“It’s sad to me that this is what’s going on,” said Bayless, an award-winning chef who runs eight popular restaurants and hosts a PBS cooking series. He said he loved the idea of being directly tied to fishermen — and the pictures and “wonderful stories” about their catch. “This throws quite a wrench in all of that.”
As part of its reporting, the AP staked out America’s largest fish market, followed trucks and interviewed fishermen who worked on three continents. During a bone-chilling week, they set up a camera that shot more than 36,000 time-lapse photos of a Montauk harbor, showing no tuna boats docking. At the same time, AP worked with a chef to order fish supposedly coming from the seaside town. The boat listed on the receipt hadn’t been there in at least two years.
Reporters also tracked Sea To Table’s supply chain to fishermen abroad who earn as little as $1.50 a day working 22-hour shifts without proper food and water.
“We were treated like slaves,” said Sulistyo, an Indonesian fisherman forced to work on a foreign trawler that delivered fish to a Sea To Table supplier. He asked that only one name be used, fearing retaliation. “They treat us like robots without any conscience.”
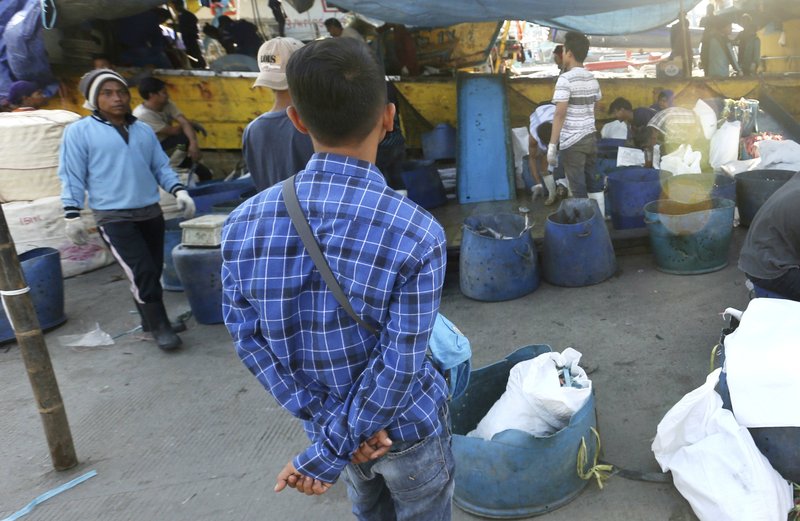
Sulistyo, left, an Indonesian fisherman who was forced to work on a foreign trawler that delivered fish to a Sea To Table supplier, watches local fisherman sort fish at a fishing port in Jakarta, Indonesia. (AP Photo/Achmad Ibrahim)
Sea To Table owner Sean Dimin emphasized his suppliers are strictly prohibited from sending imports to customers and added violators would be terminated.
“We take this extremely seriously,” he said.
Dimin said he communicated clearly with his customers that some fish labeled as freshly landed at one port was actually caught and trucked in from other states, but some chefs denied this. Federal officials described it as mislabeling.
____
A century ago, small-scale fisheries dotted America’s coasts and fed the country’s demand for seafood. But as time passed, overfishing, strict government regulations and outsourcing to developing countries changed the industry, making it nearly impossible for local fishermen to compete.
Paul Greenberg, author of “American Catch: The Fight for Our Local Seafood,” talks about the state of the seafood industry. (AP Video/Nat Castaneda)
The U.S. seafood market is worth $17 billion annually, with imports making up more than 90 percent of that. Experts say one in five fish is caught illegally worldwide, and a study last year by the University of California, Los Angeles and Loyola Marymount University found nearly half of all sushi samples tested in L.A. didn’t match the fish advertised on the menu.
Sea To Table offered a worry-free local solution that arrived from dock to doorstep by connecting chefs directly with more than 60 partners along U.S. coasts. While its mission is clear, scaling up to a national level while naming specific boats and docks is currently unrealistic. Still, the company is predicting rapid growth from $13 million in sales last year to $70 million by 2020, according to a confidential investor report obtained by the AP.
As its business expanded, AP found Sea To Table has been saying one thing but selling another.
For caterers hosting a ball for Washington Gov. Jay Inslee, who had successfully pushed through a law to combat seafood mislabeling, knowing where his fish came from was crucial.
The Montauk tuna arrived with a Sea To Table leaflet describing the romantic, seaside town and an email from a salesperson saying the fish was caught off North Carolina. But the boxes came from New York and there was no indication it had been landed in another state and driven more than 700 miles to Montauk. A week later the caterer ordered the Montauk tuna again. This time the invoice listed a boat whose owner later told AP he didn’t catch anything for Sea To Table at that time.
“I’m kind of in shock right now,” said Brandon LaVielle of Lavish Roots Catering. “We felt like we were supporting smaller fishing villages.”
Some of Sea To Table’s partner docks, it turns out, are not docks at all. Their seafood was advertised as “just landed” from wholesalers and retailers like Santa Barbara Fish Market — which also has imports — and Red’s Best in Boston. Both collect seafood at harbors and companies up and down their coasts.
Sea To Table also promoted fresh blue crab from Maryland in January, even though the season closed in November. In addition, the company said it never sells farmed seafood, citing concerns about antibiotics and hormones. But red abalone advertised from central California are actually grown in tanks — it’s been illegal to harvest commercially from the ocean since 1997. Rhode Island and Washington state also supply aquacultured seafood, such as oysters and mussels.
Dimin said farmed shellfish “is a very small part of our business, but it’s something that we’re open and clear about.” When asked to provide evidence that the company has been transparent about its use of farmed shellfish, he paused and then replied, “There’s nothing to hide there.”
However, days later, he said he decided to drop aquaculture from his business because it contradicts his “wild only” guarantee.
Private companies that mislead consumers, clients and potential investors could face lawsuits or criminal liability. Both the Food and Drug Administration and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration are charged with enforcing laws to prevent fish fraud. Sellers who know, or even should have known, that fish is mislabeled could be found guilty of conspiracy to defraud the U.S. government, mail fraud and wire fraud. The crimes carry potential fines and jail time.
Carl Safina, an award-winning author and leading marine conservationist at New York’s Stony Brook University, said companies that prey on consumers’ good intentions “deserve to be out of business immediately.”
A half dozen commercial fishermen and dealers in various regions of the country voiced concerns and, in some cases, anger about Sea To Table. Others have lashed out in the past using social media. Most spoke on condition of anonymity out of concern for their safety and their businesses in an industry where relationships often overlap.
Eric Hodge, a small-scale fisherman from Santa Barbara, said he considered partnering with Sea To Table a few years ago. He quickly changed his mind after seeing canary rockfish on the distributor’s chef lists when the fish was illegal to catch. He also learned Sea To Table was buying halibut from the fish market, which relies heavily on imports. He said he spoke to the company about his concerns.
“Honestly, they know. I just don’t think they care,” Hodge said. “They are making money on every shipment, and they are not going to ask questions. And in seafood, that’s a bad way to go about it because there is so much fraud.”
___
The idea for Sea To Table began with a family vacation to Trinidad and Tobago more than two decades ago. Following a fishing trip there, Michael Dimin and his son, Sean, eventually started shipping fresh catch from the Caribbean nation to chefs in New York. Later, they shifted their model to work exclusively with small-scale American coastal fishermen.
Restaurants and other buyers demanding sustainable products were drawn to the company by a marketing campaign that provided a story not just about where the fish came from, but the romantic image of an American pastime. And they were willing to pay a lot — sometimes more than $20 a pound — for high-end species.
The New York Times, National Geographic, Bon Appetit magazine and many others singled out Sea To Table as the good guys in a notoriously bad industry. Larry Olmsted, author of the bestselling book “Real Food, Fake Food,” recommended it as an answer to fraud in a Forbes article.
After learning about the problems, Olmsted said he was disappointed, and that it made no difference to him if part of the business was legitimate: “It either is reliable, or it’s not.”
Sea To Table partnered with sustainability giants such as the Monterey Bay Aquarium, the Marine Stewardship Council and the James Beard Foundation, which collaborated on events and referred to the distributor as an industry favorite. They expressed concern that suppliers who knowingly mislabel catch will damage the movement.
Sea To Table’s products are sold in almost every state, reaching everywhere from Roy’s seafood restaurants to Tacombi taco chain. It can be found at eateries inside the Empire State Building in New York and Chicago’s O’Hare airport, direct to consumers from its own website and even on Amazon for home cooks to order. In addition, more than 50 college campuses such as Yale, Ohio State and the University of Massachusetts have signed up. So have some of the biggest make-it-yourself meal kits, including Home Chef and Sun Basket, a rapidly growing market that Sea To Table says generates a third its revenues.
Whether they know it or not, a company spending money at any point in a long chain that begins with an abused fisherman and ends with a diner is inadvertently supporting the problem. Customers who responded to AP said they were frustrated and confused.
“Not ok,” Ken Toong, who is responsible for UMass Dining, said of Sea To Table. “We believed them.”
____
AP’s investigation began with one of Sea To Table’s nearby suppliers. Located on New York’s eastern coast beyond the posh Hamptons, Bob Gosman Company opened in Montauk as a mom-and-pop clam shack more than six decades ago.
Now run by cousins Bryan and Asa Gosman, it is a small empire sitting on a multi-million dollar property. Oceanfront restaurants, shops and motels bustle with tourists in the summer. And its fish market, where 70 percent of the tuna is imported, has become one of the biggest wholesalers in the area.
Gosman’s gets most of its tuna along with other species from a place in the state where fish can always be found, regardless of the season: The New Fulton Fish Market. The nine-acre refrigerated warehouse just outside Manhattan is the second-largest facility of its kind, moving millions of pounds of seafood each night, much of it flown in from across the globe.
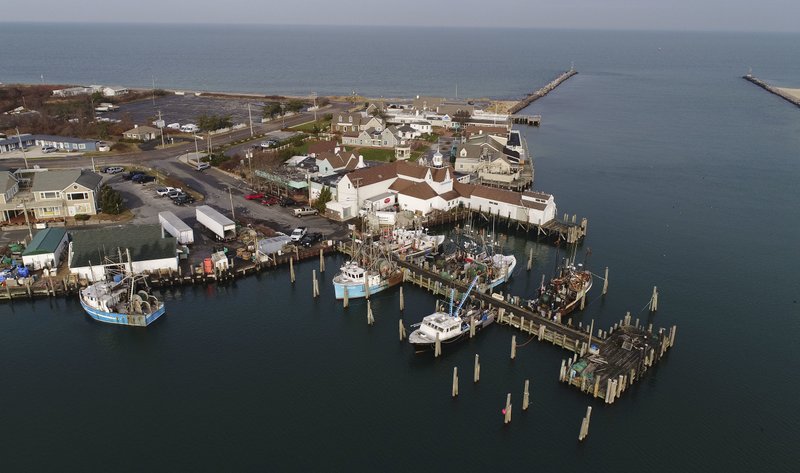

Calm waters lap up against the pilings that support some of the Bob Gosman Co. complex in Montauk, N.Y. (AP Photo/Julie Jacobson)
Beautiful maroon slabs of imported high-grade tuna were on display for several nights in December, January and February, as well as other times throughout last year, when AP reporters roamed the market. The frigid building buzzed with workers on forklifts zigzagging across slick concrete floors, stacking orders waiting to be picked up.
In the early hours, often between 2 a.m. and 4 a.m., boxes of fish bearing foreign shipping labels from all over the world were arranged into piles with “Gosman” scribbled across them in black marker. They were later hoisted onto a waiting truck with the same name.
After a three-hour drive east, the AP watched the loads arrive at the company’s loading dock in Montauk, just as the sun was rising on the tip of Long Island.
The tuna, swordfish and other species were then ferried inside Gosman’s warehouse. They came from Blue Ocean in Brazil, Vietnam’s Hong Ngoc Seafood Co., and Land, Ice and Fish in Trinidad and Tobago. Occasionally, boxes showed up from Luen Thai Fishing Venture and Marshall Islands Fishing Venture, part of a Hong Kong-based conglomerate that’s a major supplier of sushi-grade tuna. Despite recent conservation partnerships, Luen Thai has a checkered past, including shark finning and a bribery scandal that resulted in the jailing of a former Cook Islands marine resources minister in 2016.
Bryan Gosman said Sea To Table stressed it would not take imports. But with no yellowfin tuna landed in New York during the coldest winter months — which a federal official confirmed — it was impossible to provide high-quality loins from Montauk.
“So in the beginning, there were times when we were trying to hustle around fish,” Gosman said. “Buying fish at different places, so it could be a legitimate business plan that they’re trying to follow.”
Eventually, with Dimin’s blessing, Gosman said he started getting fish from as far away as North Carolina and trucking it up to New York.
They stopped that arrangement in March. Gosman said it wasn’t profitable. Dimin said they wanted to avoid the “complexity of communicating” their sourcing.
Meanwhile, in the dead of winter, AP had turned to a chef to order $500 worth of fish on their behalf. Sea To Table provided a receipt and verbal assurances that the seafood — which arrived overnight in a box bearing the company’s name and logo — had been landed in Montauk the day before.
The invoice even listed the “Standin Up” as the boat that caught it. But the vessel’s owner said it was in another state at the time, hundreds of miles away.
“I know my name is being used,” said Robert Devlin, who was upset by the news. “A lot of people do fraud that way.”
The AP also shipped tuna samples supposedly from Montauk to two labs for analysis: Preliminary DNA testing suggested the fish likely came from the Indian Ocean or the Western Central Pacific. There are limitations with the data because using genetic markers to determine the origins of species is still an emerging science, but experts say the promising new research will eventually be used to help fight illegal activity in the industry.
Bryan Gosman said they keep Sea To Table’s fish separate, but acknowledged there’s always a chance some imported tuna can slip through with domestic.
“Can things get mixed up? It could get mixed up,” he said. “Is it an intentional thing? No, not at all.”
___
The investigation didn’t end in Montauk. One of the boxes in Gosman’s stack at the Fulton fish market was stamped with a little blue tuna logo above the words “Land, Ice and Fish,” out of Trinidad and Tobago.
This is where the AP traced companies in Sea To Table’s supply chain to slave-like working conditions and the destruction of marine life.
The global seafood industry is known for providing cheap fish that comes with another price. Unscrupulous foreign companies operate with virtually no oversight in vast swaths of international waters, as AP reported in a series of stories in 2015. Those reports helped free more than 2,000 enslaved fishermen in Indonesia.
Though it’s nearly impossible to tell where a specific fish ends up, or what percentage of a company’s seafood is fraudulent, experts say even one bad piece taints the entire supply chain.
The seafood supply chain, explained. (AP Animation/Heidi Morrow)
On learning that Sea To Table’s supply chain could be tracked to businesses engaged in labor and environmental abuses, Dimin said it was “abhorrent and everything we stand against.”
He said he was temporarily suspending operations with two partners to conduct an audit.
During the investigation, reporters interviewed and obtained written complaints from more than a dozen current and former Indonesian fishermen — including Sulistyo — who were connected to companies in Sea To Table’s supply chain.
Sulistyo said his trawler plied waters between Africa and the Caribbean. Occasionally, it stopped in Trinidad and unloaded swordfish, yellowfin and bigeye tuna at Land, Ice and Fish.
Some crew members who docked there said they were beaten and forced to work when they were sick or hurt. At times, they said, migrant workers died on board and were tossed in the freezer with their catch while the boat continued to fish.
“You are out 500 miles or a thousand miles from shore, he is the law at that point,” John Duberg of Land, Ice and Fish said of individual captains. “And if he feels he has a misbehaving crew member, he may have to take disciplinary actions.”
Marine life was treated with even less respect. Some men said they were ordered to pull in as many sharks as they could catch and slice off their fins, which are a delicacy in Asia. The bodies were tossed back into the ocean, a practice banned by many countries.
Whales also were killed, their heads sometimes chopped off and their teeth extracted as good luck charms. The workers showed photos and videos of fishermen posing with mutilated sharks and whales. While some men appeared to be celebrating, others said it left them feeling sickened.
Sulistyo endured the abuse and long hours for a year before jumping to another ship in 2017, demanding to be taken to port. He returned to Indonesia and was classified as a victim of trafficking by the International Organization for Migration.
After hearing that just 30 pounds of tuna could be sold in America for more than $600 — the amount Sulistyo earned during his entire year of work — he stared at the ground in disgust.
“I want to say to the Americans who eat that fish, please appreciate what we did to catch this fish with our sweat, with our lives,” Sulistyo said. “Please remember that.”
____
AP journalists Julie Jacobson in New York and Niniek Karmini in Jakarta, Indonesia contributed to this report.